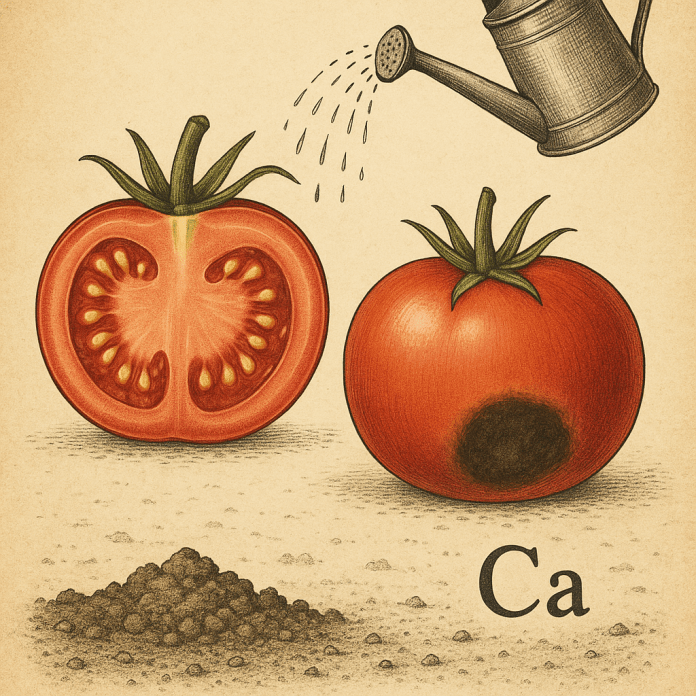
Blossom End Rot (noun; plant pathology, horticulture)
Definition:
Blossom end rot is a physiological disorder affecting the fruit of various flowering plants—most notably tomatoes, peppers, aubergines (eggplants), and courgettes (zucchini). It is characterized by a dark, sunken, leathery patch at the blossom end (opposite the stem) of developing fruit. Though often mistaken for a disease, blossom end rot is not caused by pathogens but by a calcium deficiency in the fruit tissue, often related to irregular water supply.
Etymology:
The term refers to the location and nature of the damage: the blossom end of the fruit—the part where the flower once attached—experiences rot, i.e., decay or necrosis.
Symptoms:
- Small, water-soaked spots on the blossom end of immature fruit
- Spots enlarge into sunken, leathery lesions, often dark brown or black
- Affected tissue becomes dry and papery, not slimy
- Fruits may stop growing, crack, or ripen prematurely
- Often affects the first few fruits of the season more severely
Causal Factors:
Blossom end rot results from calcium deficiency in the fruit tissue, but the problem is usually due to uneven water availability, not a lack of calcium in the soil.
Key contributing factors include:
- Irregular watering (drought followed by heavy watering)
- Overuse of high-nitrogen fertilizers
- Root damage or shallow rooting
- Excessive salinity or rapid plant growth
- Low transpiration rates (e.g., in cool, humid weather)
Susceptible Plants:
- Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum)
- Sweet pepper (Capsicum annuum)
- Chilli pepper (Capsicum spp.)
- Aubergine/Eggplant (Solanum melongena)
- Courgette/Zucchini (Cucurbita pepo)
Control and Prevention:
- Maintain consistent soil moisture: Mulch and regular watering help.
- Avoid over-fertilization, particularly with nitrogen.
- Improve soil structure to encourage even calcium uptake.
- Use calcium-rich amendments if deficiency is confirmed (e.g., garden lime or calcium nitrate).
- Grow in well-drained soil or containers with adequate root space.
- Avoid damaging roots during cultivation.
Misconceptions:
- Not a disease: No pathogen causes blossom end rot.
- Not contagious: It won’t spread between plants or fruits.
- Fungicides are ineffective: As it’s not fungal in origin, chemical sprays won’t cure it.
Impact:
Blossom end rot can significantly reduce yield and quality, especially in early fruit sets. While fruits with minor rot can be trimmed and used, severely affected ones are often discarded.