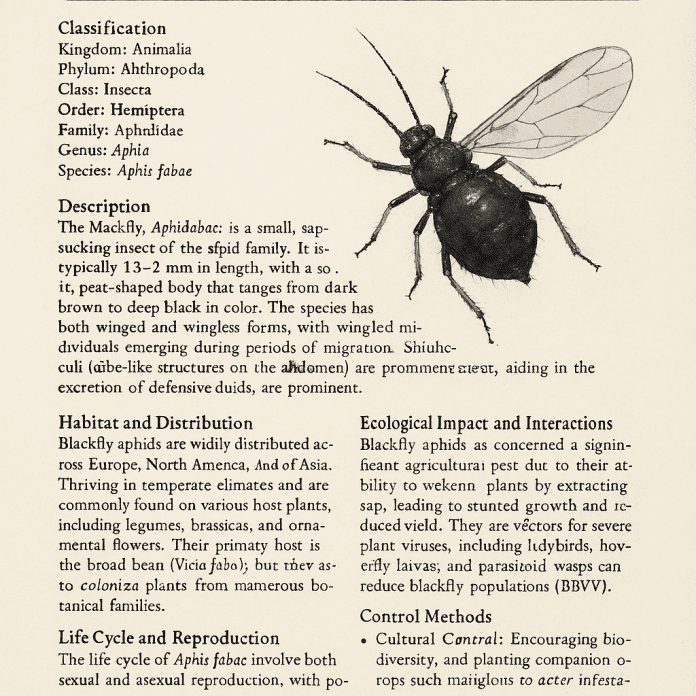
Blackfly (Aphididae: Aphis fabae Scopoli, 1763)
Classification:
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Arthropoda
- Class: Insecta
- Order: Hemiptera
- Family: Aphididae
- Genus: Aphis
- Species: Aphis fabae
Description:
The blackfly, Aphis fabae, is a small, sap-sucking insect belonging to the aphid family. It is typically 1.5–3 mm in length, with a soft, pear-shaped body that ranges from dark brown to deep black in color. The species has both winged and wingless forms, with winged individuals emerging during periods of migration. The antennae are relatively short, and siphunculi (tube-like structures on the abdomen) are prominent, aiding in the excretion of defensive fluids.
Habitat and Distribution:
Blackfly aphids are widely distributed across Europe, North America, and parts of Asia. They thrive in temperate climates and are commonly found on various host plants, including legumes, brassicas, and ornamental flowers. Their primary host is the broad bean (Vicia faba), but they also colonize plants from numerous botanical families.
Life Cycle and Reproduction:
The life cycle of Aphis fabae involves both sexual and asexual reproduction, with populations undergoing cyclic parthenogenesis. In spring, overwintering eggs hatch into wingless females that reproduce clonally, giving birth to live offspring without mating. As summer progresses, some offspring develop into winged forms, dispersing to new host plants. In late autumn, sexual forms appear, leading to the production of overwintering eggs.
Ecological Impact and Interactions:
Blackfly aphids are considered a significant agricultural pest due to their ability to weaken plants by extracting sap, leading to stunted growth and reduced yield. They are also vectors for several plant viruses, including Bean Yellow Mosaic Virus (BYMV) and Broad Bean Stain Virus (BBSV). Their presence often attracts natural predators such as ladybirds (Coccinellidae), lacewings (Chrysopidae), and parasitic wasps (Aphidiinae), which help regulate populations.
Control Methods:
- Cultural Control: Encouraging biodiversity and planting companion crops such as marigolds can deter aphid infestations.
- Biological Control: Introducing natural predators like ladybirds, hoverfly larvae, and parasitoid wasps can reduce blackfly populations.
- Chemical Control: In cases of severe infestation, insecticidal soaps or plant-based treatments (e.g., neem oil, where legal) may be used.
- Physical Control: Manually removing aphids or using water sprays can help manage small infestations.
Historical Context:
The species Aphis fabae was first described by Giovanni Antonio Scopoli in 1763. The inclusion of the author’s name and year of description follows standard taxonomic conventions, providing historical and scientific context for its classification.
Conclusion:
Despite their role as agricultural pests, blackfly aphids are an integral part of many ecosystems, providing a food source for beneficial insects. Sustainable management strategies that balance pest control with ecological preservation are crucial for maintaining plant health and biodiversity.