Apetalous
Definition:
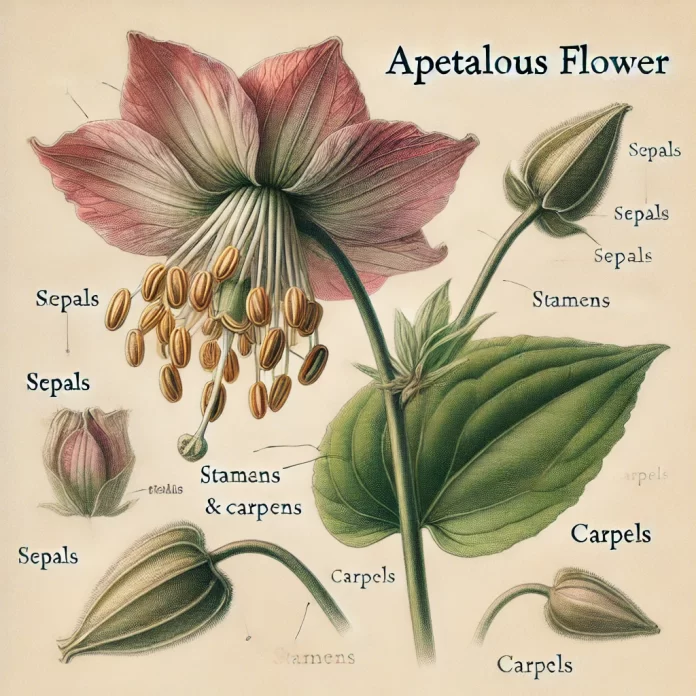
Apetalous (from the Greek a- meaning “without” and petalon meaning “petal”) describes a flower that lacks petals.
Botanical Context:
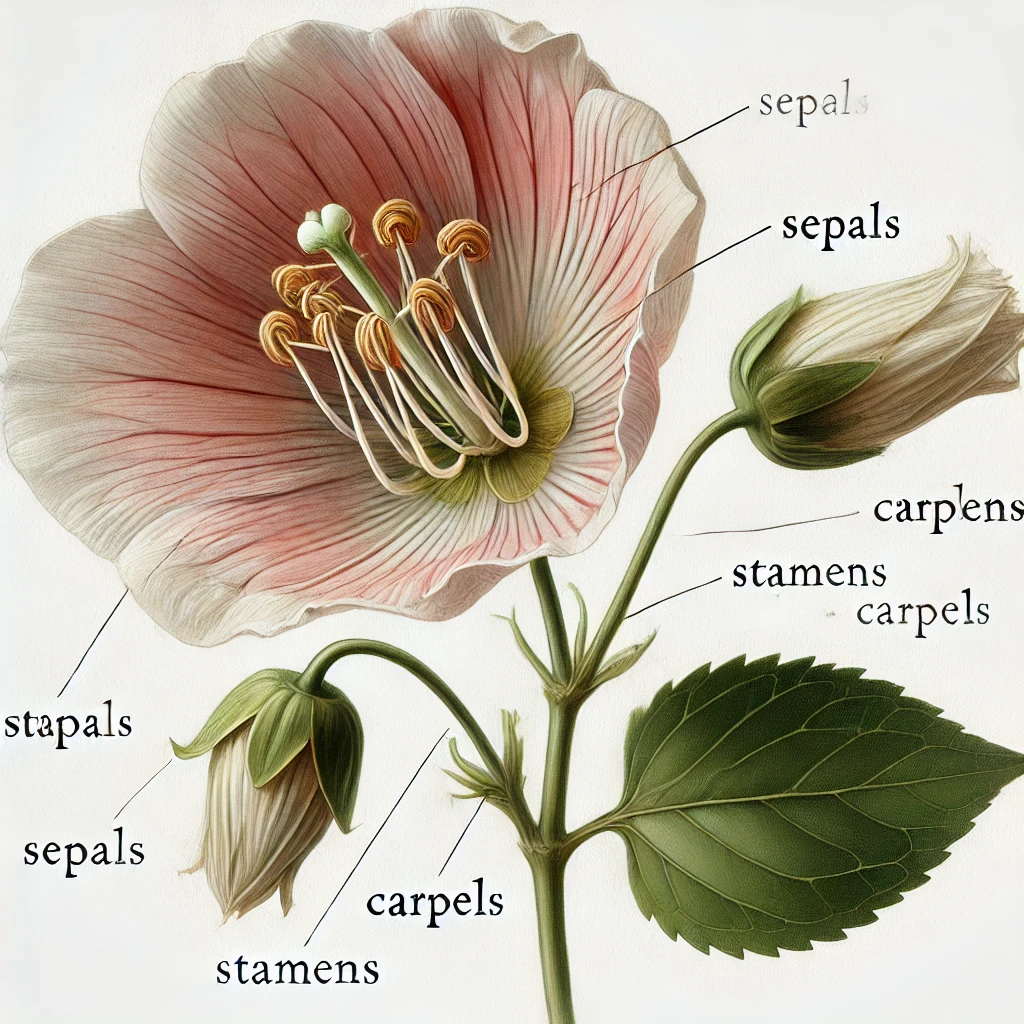
In botanical classification, apetalous flowers are those that do not develop petals, though they may still possess other floral structures such as sepals, stamens, and carpels. This characteristic can be an evolutionary adaptation to wind or insect pollination, where petals are unnecessary for attracting pollinators.
Examples in Plant Families:
- Salicaceae (Willow Family): Willows (Salix spp.) and poplars (Populus spp.) produce small, apetalous flowers arranged in catkins, relying on wind or insect pollination.
- Amaranthaceae (Amaranth Family): Many species, including those in Chenopodium (goosefoot) and Amaranthus (amaranth), exhibit apetalous flowers.
- Urticaceae (Nettle Family): The stinging nettle (Urtica dioica) has small, greenish, apetalous flowers adapted for wind pollination.
Pollination and Adaptations:
Apetalous flowers often rely on alternative strategies for reproduction:
- Wind Pollination (Anemophily): Without showy petals, these flowers produce abundant, lightweight pollen that is carried by the wind (e.g., grasses and many trees).
- Inconspicuous Insect Pollination (Entomophily): Some apetalous species still attract pollinators through nectar or scent rather than visual cues.
- Cleistogamy: Some apetalous flowers, such as those in Viola species, are self-pollinating and remain closed throughout pollination.
Distinction from Sepal-Lacking Flowers:
Apetalous flowers may still retain sepals (calyx), which can sometimes be petal-like in function, as seen in many Euphorbia species. If a flower lacks both petals and sepals, it is described as achlamydeous.
This trait is significant in understanding plant morphology, ecology, and pollination strategies, demonstrating how different species evolve to thrive in various environmental conditions.