Anther
Definition
The anther is the pollen-producing part of a stamen, the male reproductive organ of a flower. It is typically located at the tip of the filament and plays a crucial role in plant reproduction by releasing pollen for fertilization.
Structure and Function
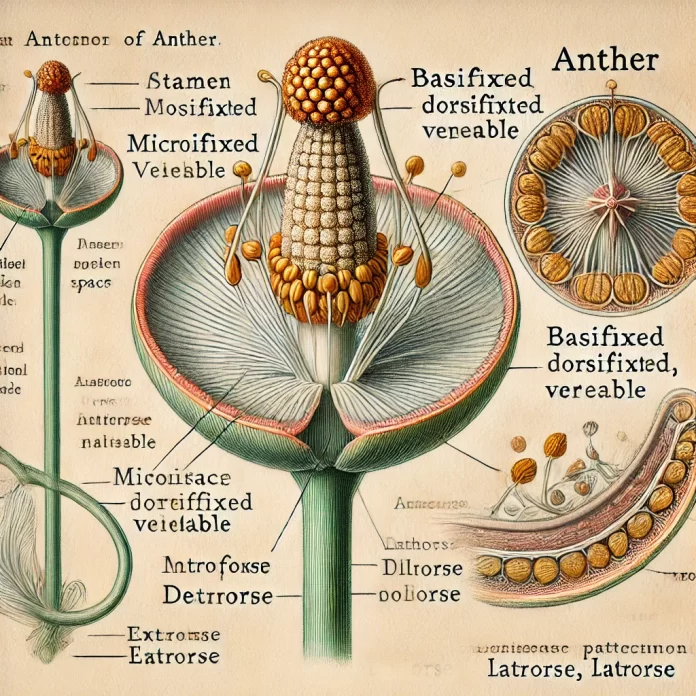
- Usually consists of two lobes, each containing two pollen sacs (microsporangia).
- Pollen is produced within these sacs and released when the anther dehisces (splits open).
- Anther attachment varies; it may be basifixed (attached at the base), dorsifixed (attached at the center), or versatile (able to move freely).
Types of Anthers
- Extrorse – Opens outward, releasing pollen away from the flower center.
- Introrse – Opens inward, releasing pollen toward the center.
- Latrorse – Opens sideways.
Importance in Pollination
- Essential in pollination, as pollen must reach a compatible stigma for fertilization.
- Pollen dispersal methods vary (e.g., wind, insects, birds).
- Some anthers have adaptations such as pores or slits for controlled pollen release.
The anther, together with the filament, forms the stamen, the fundamental male reproductive unit of a flower.