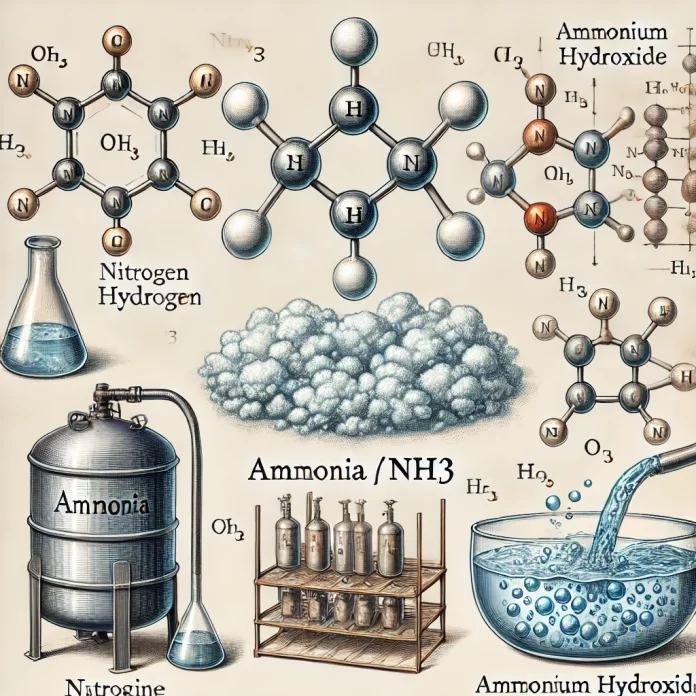
Ammonia
Chemical Formula: NH₃
Definition:
Ammonia is a colorless, pungent gas composed of nitrogen and hydrogen. It is a naturally occurring compound found in the environment, animal waste, and biological processes. Ammonia is widely used in agriculture, industry, and household cleaning products.
Physical & Chemical Properties:
- State: Gas at room temperature
- Odor: Strong, sharp, and pungent
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water, forming ammonium hydroxide (NH₄OH)
- Boiling Point: -33.34°C (-28.01°F)
- pH: Basic (alkaline) in aqueous solution
Natural Occurrence & Production:
Ammonia is produced naturally through the decomposition of organic matter, nitrogen fixation by bacteria, and metabolic processes in animals and plants. Industrially, it is synthesized using the Haber-Bosch process, which combines nitrogen and hydrogen under high pressure and temperature.
Uses & Applications:
- Agriculture: Used in fertilizers (ammonium nitrate, urea) to supply nitrogen for plant growth.
- Chemical Industry: A precursor in the production of nitric acid, explosives, and synthetic fibers.
- Cleaning Products: Found in household and industrial cleaners due to its grease-cutting and disinfectant properties.
- Refrigeration: Used as a refrigerant gas (R717) in industrial cooling systems.
- Water Treatment: Helps neutralize acidic contaminants and is used in wastewater treatment.
Health & Environmental Impact:
- Exposure Risks: High concentrations can cause irritation to the eyes, nose, throat, and lungs. Severe exposure may lead to respiratory distress or chemical burns.
- Environmental Effects: Ammonia released into the environment can contribute to eutrophication in water bodies, affecting aquatic ecosystems. However, it is also a vital component of the nitrogen cycle.
See Also:
- Haber-Bosch Process
- Ammonium Compounds
- Nitrogen Cycle