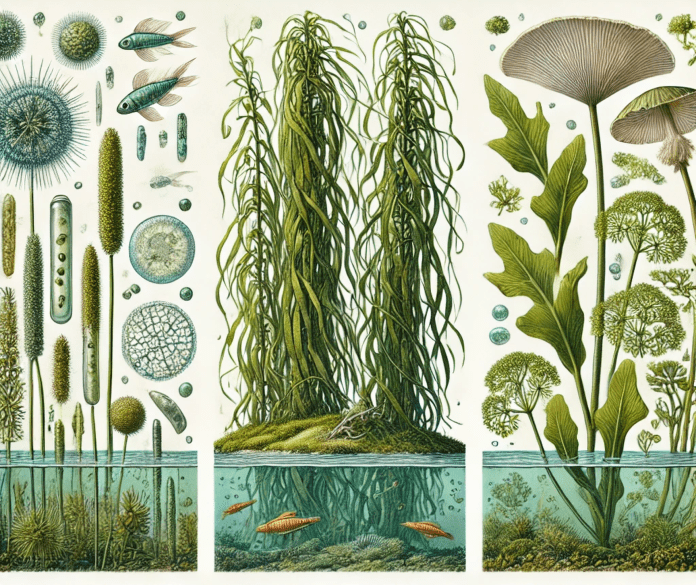
Definition:
Algae are a diverse group of photosynthetic organisms found in aquatic and moist terrestrial environments. They range from microscopic, single-celled forms like phytoplankton to large multicellular forms like seaweeds. While not true plants, algae play a vital role in ecosystems as primary producers.
Examples of Algae:
- Microscopic Algae: Diatoms and dinoflagellates found in freshwater and marine ecosystems.
- Macroscopic Algae: Kelp (Macrocystis pyrifera) and green algae (Ulva), commonly known as sea lettuce.
Significance in Botany and Ecology:
- Photosynthesis: Algae produce a significant portion of the world’s oxygen and serve as the base of aquatic food webs.
- Habitat Formation: Large algae, like kelp, create underwater forests that support diverse marine life.
- Human Uses: Algae are used for food (e.g., nori), biofuels, fertilizers, and pharmaceuticals.
Etymology:
Derived from the Latin word alga, meaning “seaweed.”