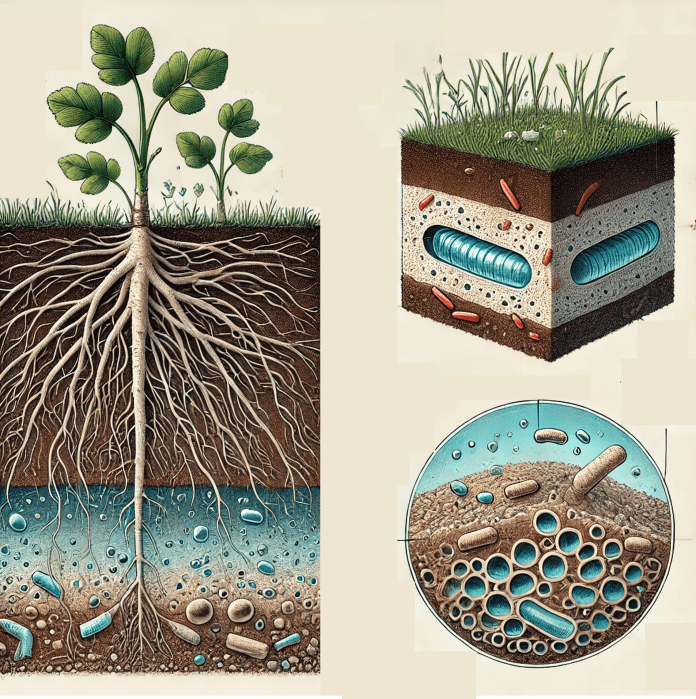
Definition:
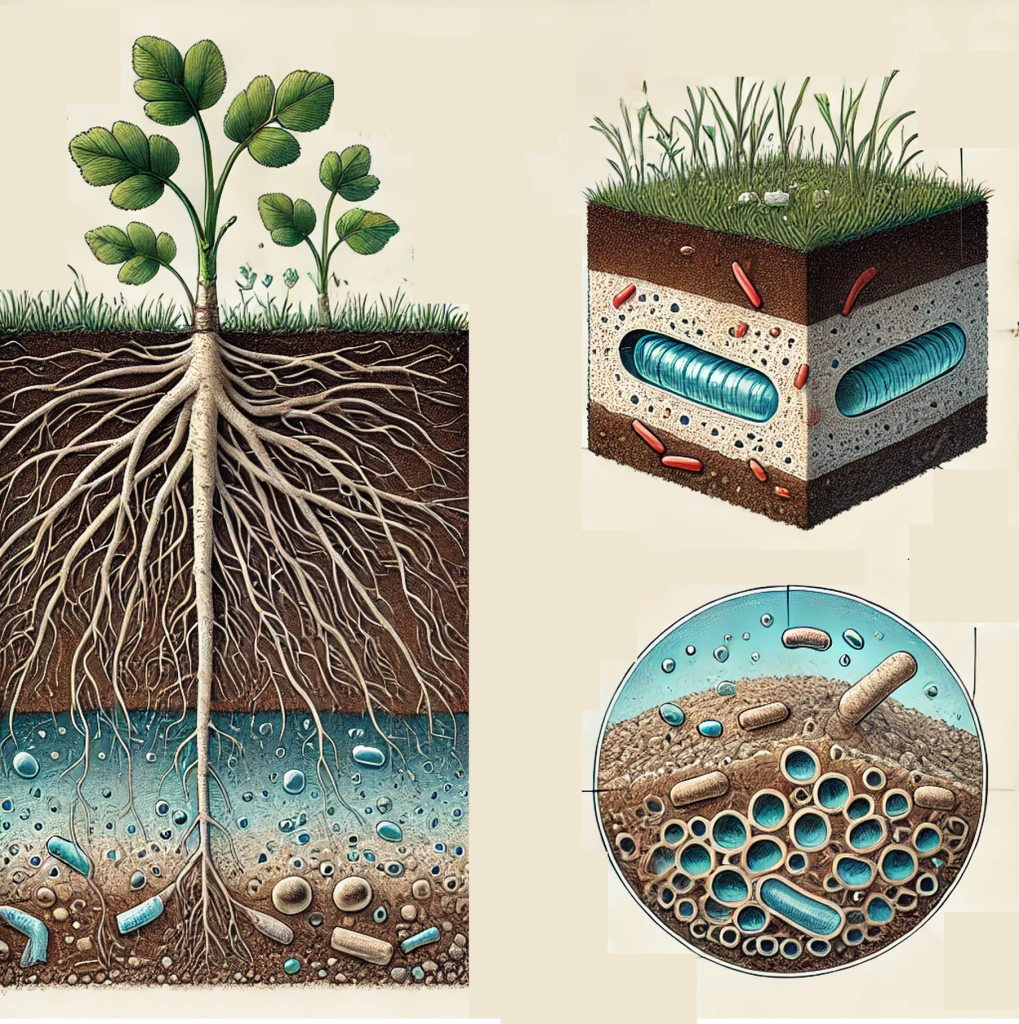
Aerobic refers to processes or organisms that require oxygen to survive, grow, or function. In plants and soils, aerobic conditions are essential for various biological activities, such as respiration, nutrient cycling, and microbial activity.
Examples in Plants and Soils:
- In Plant Respiration: Roots in well-aerated soils utilize oxygen for cellular respiration, providing energy for growth.
- In Soils: Aerobic microbes decompose organic matter, releasing nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus essential for plant health.
Significance in Botany:
Aerobic conditions promote healthy root systems, efficient nutrient uptake, and thriving microbial communities in the soil. Poor aeration leads to anaerobic conditions, which can cause issues like root rot and reduced plant vigor.
Etymology:
Derived from the Greek words aēr (air) and bios (life), meaning “living in air.”