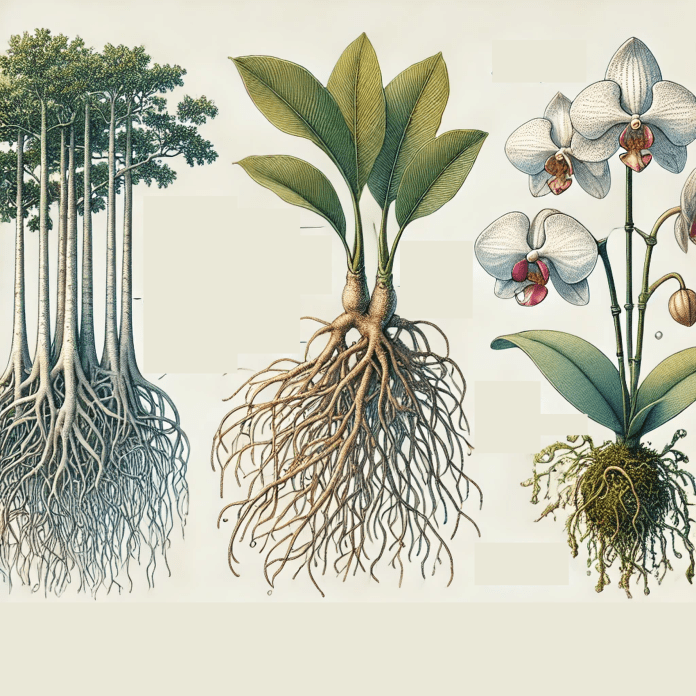
Definition:
Aerial roots are roots that grow above the ground or water, often exposed to the air. These roots are specialized for various functions, such as structural support, gas exchange, water absorption, or nutrient acquisition, depending on the plant species.
Examples in Plants:
- Structural Support: Prop roots in plants like Ficus benghalensis (banyan tree).
- Gas Exchange: Pneumatophores in mangroves, such as Avicennia marina.
- Water Absorption: Epiphytic plants like orchids (Phalaenopsis species) use aerial roots to absorb moisture from the air.
Significance in Botany:
Aerial roots allow plants to thrive in challenging environments, such as waterlogged soils, rocky terrains, or as epiphytes on other plants. They are adaptations that provide stability, access to nutrients, and oxygen exchange, crucial for survival in diverse habitats.
Etymology:
Derived from the Latin word aer, meaning “air,” and the Old English word rōt, meaning “root.”