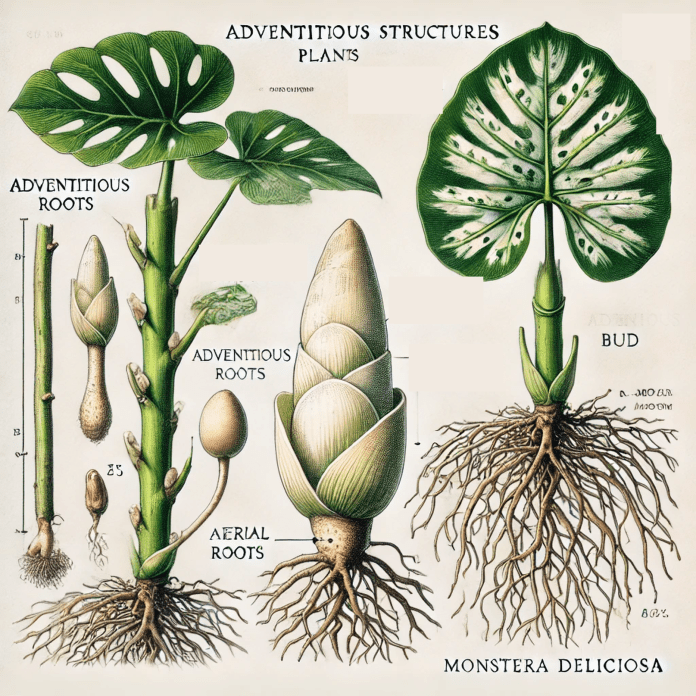
Definition:
Adventitious refers to structures, particularly roots, that arise in unusual or unexpected locations on a plant, such as from stems, leaves, or other non-root tissues. These structures are not part of the plant’s primary development from the embryo but develop in response to environmental conditions, injury, or specific growth needs.
Examples in Plants:
- Adventitious roots: Roots forming from stem cuttings, such as in Ficus pumila (creeping fig) or when aerial roots emerge on plants like Monstera deliciosa.
- Adventitious buds: Buds that develop on roots, as in the case of suckering plants like blackberries (Rubus fruticosus).
Significance in Botany:
Adventitious structures are often associated with the plant’s ability to adapt to stress, propagate vegetatively, or survive challenging environmental conditions. For example, adventitious rooting is a key process in the propagation of many horticultural plants.
Etymology:
Derived from the Latin word adventicius, meaning “coming from outside” or “extraneous.”